Advanced scoliosis care by professor
Hany Abdel Gawwad
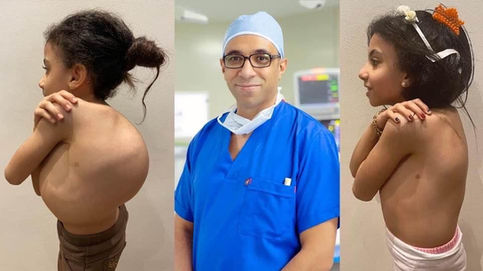
Advanced scoliosis care by professor Hany Abdel Gawwad, where we provide advanced and compassionate care for individuals facing the challenges of scoliosis and more complex conditions like kyphosis. Our dedicated team of experts is committed to enhancing lives through personalized treatment plans and state-of-the-art medical interventions.



TYPES OF SCOLIOSIS
-
Idiopathic Scoliosis : The most prevalent type, with no definite cause.
-
Congenital Scoliosis : Present at birth due to spinal deformities.
-
Neurological Scoliosis : Caused by nerve abnormalities affecting spine muscles.
-
Structural Scoliosis : Permanent deformity from injury, disease, or birth defects.
-
Non-structural Scoliosis : Temporary curves that can be corrected.
TYPES OF KYPHOSIS
-
Postural Kyphosis : Caused by poor posture and can often be corrected with lifestyle changes.
-
Scheuermann's Kyphosis : Develops during adolescence and involves structural changes in the spine.
-
Congenital Kyphosis : Present at birth due to spinal malformations.
-
Age-Related Kyphosis : Occurs in older adults due to degenerative changes in the spine.
WHAT IS SCOLIOSIS︖
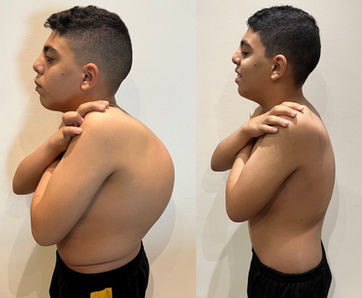
Scoliosis is a common condition characterized by a sideways curvature of the spine, often emerging during puberty. While its origins can vary, most cases are mild. However, without proper attention, severe deformities may lead to significant functional disabilities, impacting lung function and overall well-being.
.jpeg)
SYMPTOMS
Uneven shoulders
Prominent shoulder blade
Uneven waist
Asymmetrical hip levels
IDENTIFYING KYPHOSIS
Rounded Shoulder
Hump on the upper back
Back pain or stiffness
Fatigue and muscle weakness
RISKS
-
Onset during the growth spurt before puberty.
-
Higher risk for girls than boys.
-
Familial connections, though most cases lack a family history
COMPLICATIONS
-
Lung and heart damage due to rib cage pressure.
-
Back problems, especially in adults with scoliosis.
-
Noticeable changes in posture and body symmetry
TREATMENT OPTIONS
The severity of scoliosis determines the course of treatment, considering factors such as :
-
Age
-
Body Growth
-
Genetics
-
Curve type
TREATMENT
(For curvature below 25 to 40 degrees)
-
Underarm Brace : Virtually invisible, suitable for lower spine curves.
-
Milwaukee Brace : Covers the torso, ideal for extensive spinal support.
.jpeg)
Advanced surgical
ADVANCED SURGICAL PROCEDURE
-
(For significant curves beyond 40 degrees)
-
Spinal Fusion : Fuses vertebrae using bone grafts, rods, and screws.
-
The rods keep the spine in a straight position, and the screws hold them in place. The bone graft and vertebrae fuse into a single bone, and the rods can be adjusted in children with age.
CAUSES
-
Poor posture
-
Osteoporosis
-
Degenerative disc disease
-
Spinal fractures
-
Congenital abnormalities
-
Hereditary factors play a role.
-
Neuromuscular conditions like cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy.
-
Birth defects influencing spinal bone development.
-
Spine injuries or infections.